문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17352
17352번: 여러분의 다리가 되어 드리겠습니다!
선린월드에는 N개의 섬이 있다. 섬에는 1, 2, ..., N의 번호가 하나씩 붙어 있다. 그 섬들을 N - 1개의 다리가 잇고 있으며, 어떤 두 섬 사이든 다리로 왕복할 수 있다. 어제까지는 그랬다. "왜 다리
www.acmicpc.net
사용 언어
Python3
풀이 과정
일단... 이 문제는 혼자 풀긴 풀었는데 Python3로 채점도 성공했지만 시간도 오래걸리고 무엇보다 공간복잡도가 극악이었다. (예상하지 못한게 문제)
그리고 처음엔 계속 10%대에서 틀렸습니다가 떴는데 따라서 열심히 반례를 찾았다.
# 두 개로 나눠진 영역의 양 끝단 중 아무거나 이어주면 됨
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
input = sys.stdin.readline
def solution(graph, visited, island):
visited[island] += 1
for i in graph[island]:
if visited[i] == 0:
solution(graph, visited, i)
else:
visited[i] += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = int(input())
graph = {x: [] for x in range(1, N + 1)}
for _ in range(N-2):
i1, i2 = map(int, input().split())
graph[i1].append(i2)
graph[i2].append(i1)
visited = [0] * (N + 1)
solution(graph, visited, 1)
a = visited.index(1)
next = visited.index(0, a + 1)
solution(graph, visited, next)
b = visited.index(1, next)
print(a, b)위의 코드대로면 아래와 같은 경우에는 다음으로 다시 탐색할 시작점 b를 찾을 수 없게 된다.
7
1 3
1 4
1 5
1 6
1 7
그런데 next 찾는 범위를 변경하면 b를 찾기도 어려워져서 고민하다가 그냥 visited를 두 개로 만들어서 해결해버렸다. 이 부분 때문에 공간복잡도가 더 심각해진 것 같긴 한데 일단.. 맞추고 싶어서 제출했더니 맞았습니다!!
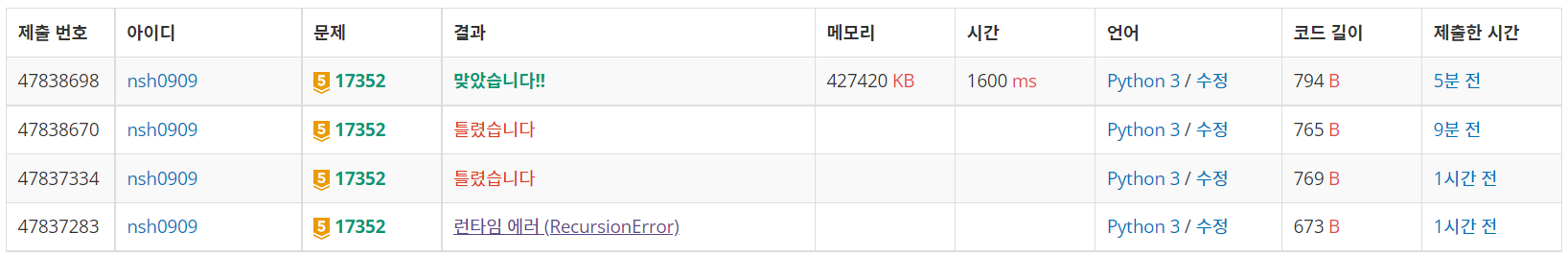
이 코드를 살릴려면(?) 일단 DFS를 BFS로 변경하고 visited 참조하는 부분을 손봐야할 것 같다.
제출 답안
# 두 개로 나눠진 영역의 양 끝단 중 아무거나 이어주면 됨
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
input = sys.stdin.readline
def solution(graph, visited, island):
visited[island] += 1
for i in graph[island]:
if visited[i] == 0:
solution(graph, visited, i)
else:
visited[i] += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = int(input())
graph = {x: [] for x in range(1, N + 1)}
for _ in range(N-2):
i1, i2 = map(int, input().split())
graph[i1].append(i2)
graph[i2].append(i1)
visited1 = [0] * (N + 1)
visited2 = [0] * (N + 1)
solution(graph, visited1, 1)
a = visited1.index(1)
next = visited1.index(0, 1)
solution(graph, visited2, next)
b = visited2.index(1)
print(a, b)코드 개선
1. BFS 방식으로 변경
# 두 개로 나눠진 영역의 양 끝단 중 아무거나 이어주면 됨
from collections import deque
from sys import stdin
input = stdin.readline
def solution(graph, visited, island):
q = deque([island])
while q:
i = q.popleft()
if visited[i] == 0:
q.extend(graph[i])
visited[i] += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = int(input())
graph = {x: [] for x in range(1, N + 1)}
for _ in range(N-2):
i1, i2 = map(int, input().split())
graph[i1].append(i2)
graph[i2].append(i1)
visited1 = [0] * (N + 1)
visited2 = [0] * (N + 1)
solution(graph, visited1, 1)
a = visited1.index(1)
next = visited1.index(0, 1)
solution(graph, visited2, next)
b = visited2.index(1)
print(a, b)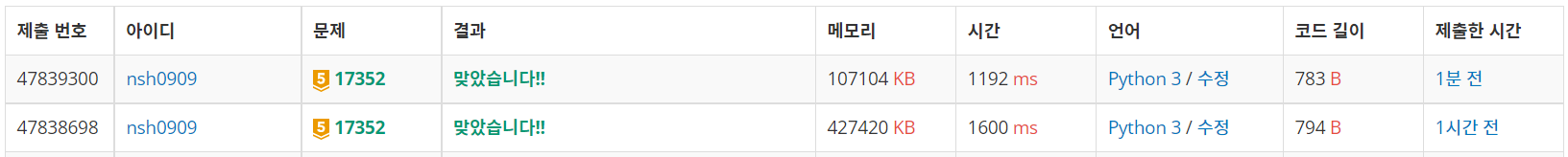
➡ 시간복잡도와 공간복잡도 모두 의미 있는 차이를 보였다! 그래도 여전히 높은 편인것 같기 때문에 추가로 수정이 필요해보였다.
2. visited return으로 변경
# 두 개로 나눠진 영역의 양 끝단 중 아무거나 이어주면 됨
from collections import deque
from sys import stdin
input = stdin.readline
def solution(graph, island):
q = deque([island])
visited = [0] * (N + 1)
while q:
i = q.popleft()
if visited[i] == 0:
q.extend(graph[i])
visited[i] += 1
return visited
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = int(input())
graph = {x: [] for x in range(1, N + 1)}
for _ in range(N-2):
i1, i2 = map(int, input().split())
graph[i1].append(i2)
graph[i2].append(i1)
visited1 = solution(graph, 1)
a = visited1.index(1)
next = visited1.index(0, 1)
visited2 = solution(graph, next)
b = visited2.index(1)
print(a, b)
➡ 결국 solution함수를 돌릴 때마다 visited를 새로 만들어서 사용하는건 똑같은데 괜히 return하는 부분이 추가되어 오히려 늘어난 것 같다...
이 방식대로 풀려면 어쨌든 나눠진 두 영역으로 함수를 돌린 후 각각의 visited 리스트에서 1이 어디있는지를 체크하는 게 필요한데 더 줄이는 게 힘들어보여서 아예 다른 문제 풀이 접근 방식을 찾아봤다.
다른 사람 코드
찾아보니 이게 일반적인 Union-Find 알고리즘 문제라고 한다.
사실 처음 문제를 읽었을 때 직사각형의 세 꼭짓점 좌표로 나머지 한 좌표를 찾는 문제에서 비트 연산을 사용하는 게 생각났는데, 이 문제는 정점이 많이 때문에 적용하지 못했다. 대신 Union-Find라는 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있는 거였군..!
결국 이 문제는 신장트리에서 마지막 하나의 간선을 그리는 방법으로 트리간 가중치가 존재하지 않기 때문에 Union-Find로 풀 수 있다고 한다. 코드는 두 가지를 돌려보았는데 둘 다 내 것 보단 훨씬 빨랐다ㅎㅎ
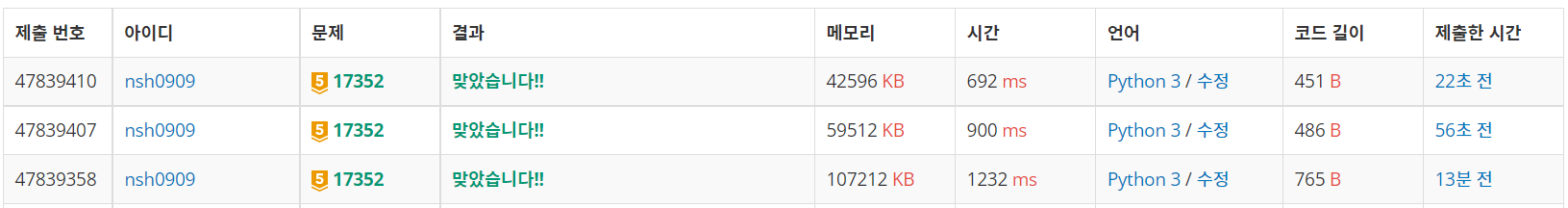
둘 다 전체적인 흐름은 다음과 같은 것 같다.
1. 먼저 입력으로 주어진 n-2개의 정보들에 대해 union 연산을 수행한다음
2. 임의의 정점 한개를 잡아서 (이 코드에서는 1을 임의의 정점으로 설정)
3. n개의 정점들에 대해서 union 할 필요가 있는지 여부를 검사하고
4. 만약 부모노드가 달라서 union 할 필요가 있는 경우
5. 임의의 시작 정점과 해당 정점을 정답으로 하여 출력한다.
1. 900ms
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
def find(x):
if parent[x] == x:
return x
parent[x] = find(parent[x])
return parent[x]
def union(a, b):
a = find(a)
b = find(b)
if a < b:
a, b = b, a
parent[b] = a
N = int(input())
parent = {i: i for i in range(1, N+1)}
for _ in range(N-2):
a, b = map(int, input().split())
union(a, b)
pivot = find(1)
for i in range(2, N+1):
if pivot != find(i):
print(pivot, i)
exit()출처 : https://devlibrary00108.tistory.com/535
2. 692ms
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
def find_p(x):
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find_p(p[x])
return p[x]
else:
return x
n = int(input())
p = [i for i in range(n+1)]
for _ in range(n-2):
i1, i2 = map(int, input().split())
p1 = find_p(i1)
p2 = find_p(i2)
if p1 == p2:
continue
p[p1] = p2
ans_island = []
for i in range(1, n+1):
if i == p[i]:
ans_island.append(i)
print(*ans_island)출처 : https://amaranth1ne.tistory.com/39
'코딩 테스트 스터디 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [실버 I] 11286번. 절댓값 힙 (0) | 2022.08.24 |
|---|---|
| [실버 II] 1541번. 잃어버린 괄호 (0) | 2022.08.23 |
| [실버 III] 17626번. Four Squares (0) | 2022.08.16 |
| [골드 V] 5430번. AC (0) | 2022.08.12 |
| [실버 III] 15650번. N과 M (2) (0) | 2022.08.11 |